Classical Music
Please put on your headphone for the best experience
Navigating with arrow keys or by clicking menus on the bottom right corner

Vuong Trung Hieu
vuongg@protonmail.com
È il sol dell'anima - Joan Sutherland, Luciano Pavarotti
Outline
Instruments of the Orchestra
The History of Classical music
Classical music genres
The History of Classical music
Medieval music (500 – 1400)
Ancient music period (before 500 A.D)
Renaissance (1400 – 1600)
Baroque (1600 – 1750)
Classical (1750 – 1820)
Romantic (1820 – 1900)
20th and 21st centuries (1900 - present)
Ancient music period (before 500 A.D)
designated by the characterization of the basic notes and scales
transmitted through oral or written systems
Medieval music (500 – 1400)
written for the church was almost always vocal (singing)
Medieval composers who are remembered today include Léonin, Pérotin and Guillaume de Machaut
Renaissance (1400 – 1600)
a massive increase in the composition of music, both sacred (church) and secular (not having any connection with religion)
The greatest composers of this period include: Giovanni da Palestrina, Orlando di Lasso, Thomas Tallis and William Byrd
Baroque (1600 – 1750)
The greatest composers of this time include: Claudio
Monteverdi, Heinrich Schütz, Henry Purcell, Antonio
Vivaldi, George Frideric Handel, Johann Sebastian Bach,
Domenico Scarlatti and Georg Philipp Telemann
Baroque (1600 – 1750)
The modern orchestra was formed
The opera was invented
Classical (1750 – 1820)
The greatest composers include: Joseph Haydn, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Christoph Willibald Gluch, and Ludwig van Beethoven
Classical (1750 – 1820)
Composers thought a lot about the forms of their pieces and were influenced by the classical art of the Ancient Greeks and Romans
The symphony was invented and various forms of chamber music
Romantic (1820 – 1900)
Some of the greatest composers include: Ludwig van Beethoven, Franz Schubert, Hector Berlioz, Frédéric Chopin, Robert Schumann, Felix Mendelssohn, Anton Bruckner, Johannes Brahms, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky, Edward Elgar, Gustav Mahler and Richard Strauss
Romantic (1820 – 1900)
Personal feeling and emotion
Music for orchestra sometimes told a story
It was a time when there were a lot of changes in society. There was a lot of feeling of nationalism as countries united
19th century music is often nationalistic: composers wrote music that was typical of their own country
20th and 21st centuries (1900 - present)
Some of the most important composers are: Claude Debussy, Jean Sibelius, Maurice Ravel, Arnold Schoenberg, Igor Stravinsky, Béla Bartók, Aaron Copland, Benjamin Britten, Dmitri Shostakovich, Leonard Bernstein, Philip Glass, Dmitri Kabalevsky, James MacMillan, Judith Weir, Peter Maxwell Davies
20th and 21st centuries (1900 - present)
Composers wanted to find new ways of composing
Classical music was influenced by jazz, especially with American composers
Today’s composers have developed their own styles
Modernist (1890 – 1950) that overlaps from the late-19th
century
- Impressionism (1890 – 1925)
- Expressionism (1908 – 1925)
- Neoclassicism (1920 – 1950)
Postmodern era/Contemporary (1930 – present)
- Experimental (1950 – present)
- Minimalism (1965 – present)
The History of Classical music
Instruments of the Orchestra
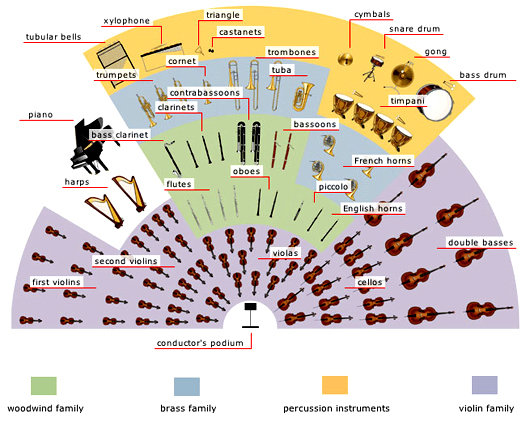
Instruments of the Orchestra

Conductor
Strings section

Strings section

Woodwind section
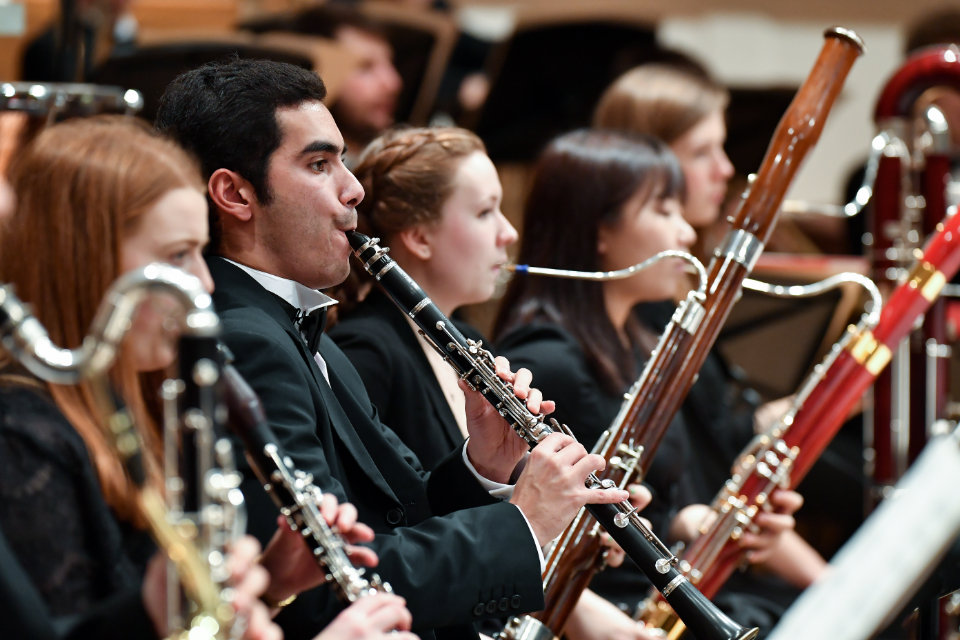

Woodwind section

Brass section
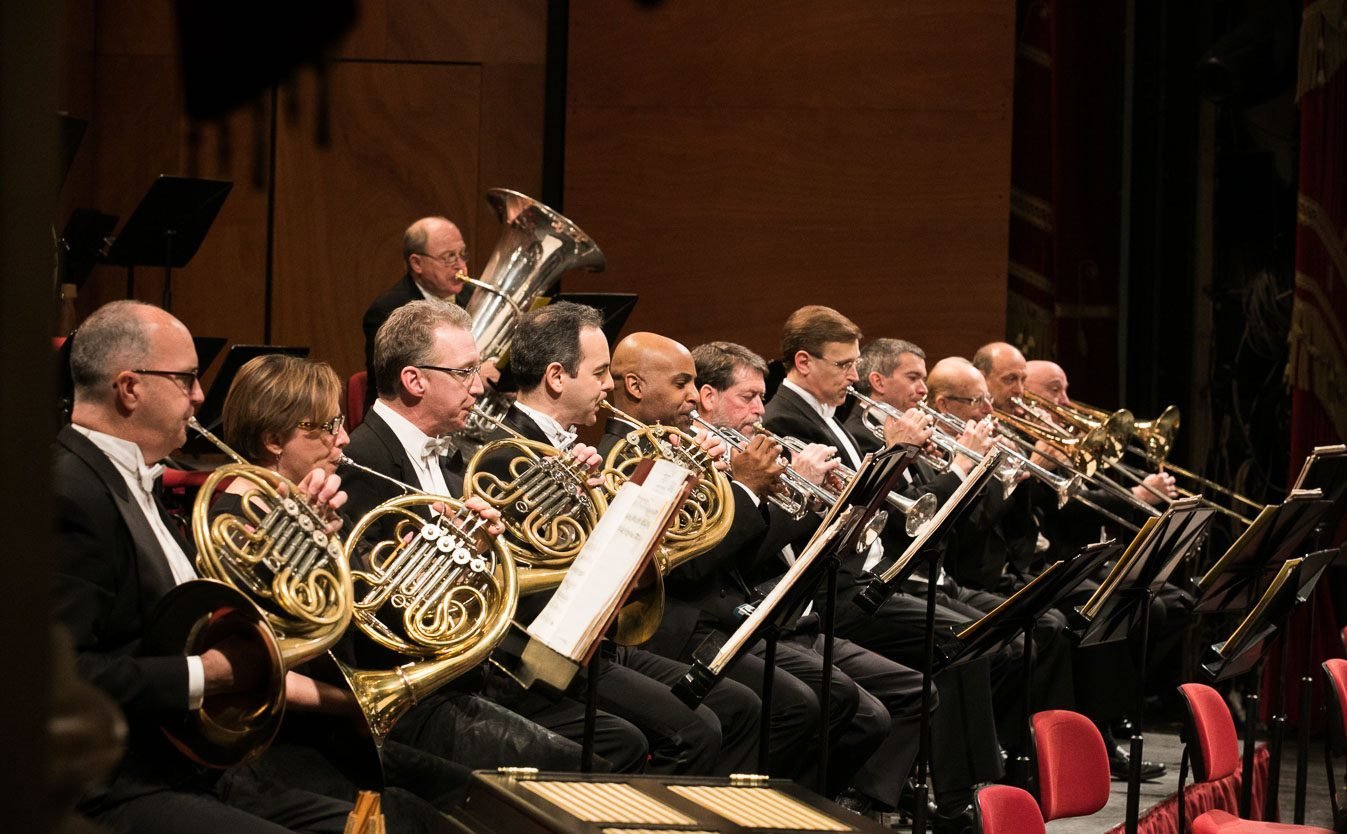

Brass section

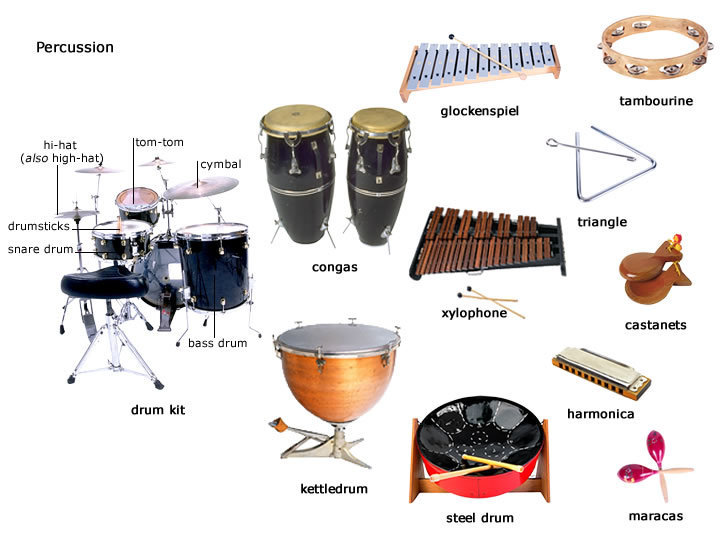
Percussion section
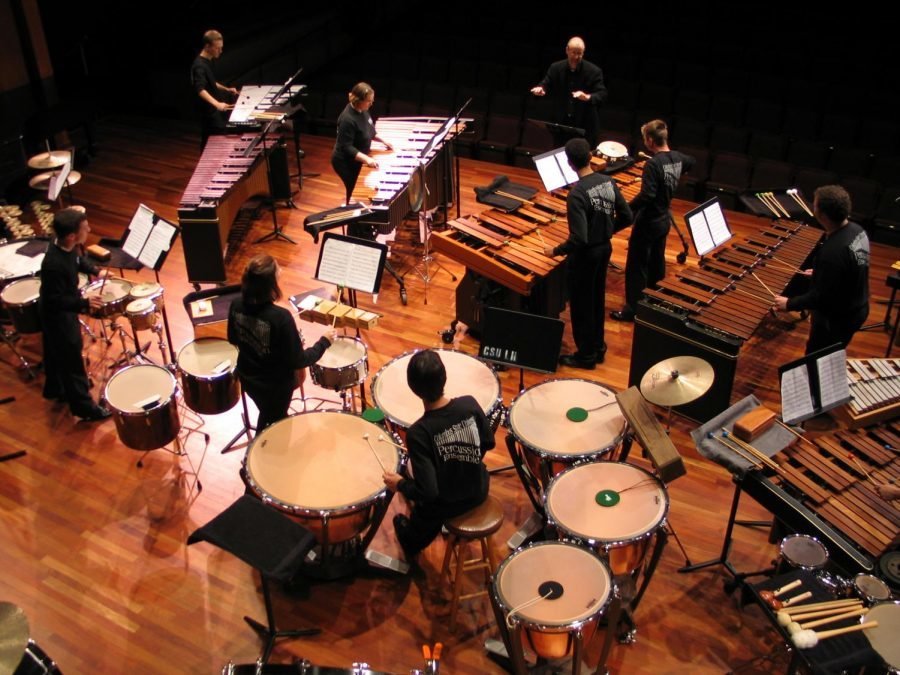

Percussion section
Classical music genres
Movement in Classical music
What is a movement?
— a self-contained part of a musical composition
— Long pieces of classical music are often divided into movements
— “Satz” is the German word for “movement” (in this musical sense), which really means “sentence”
Classical music genres
Sonata
— is a piece of music for one instrument or one instrument with another instrument accompanying.
— usually is quite a long piece with several movements.
— The word “sonata” comes from Italian word “sonare” (to sound).
Beethoven — Moonlight Sonata 1st movement
Classical music genres
Cantata
— is a type of singing which is done accompanied by an instrument(s).
— The word “cantata” comes from Italian word “cantare” (to sing).
Johann Sebastian Bach — BMV 29
Classical music genres
Étude
— is a short piece of music written to help the player to become a better player.
— usually quite difficult to play.
Etude Op. 10 No. 4 Torrent (Chopin)
Classical music genres
Rhapsody
— is a piece of music that has no formal structure and expresses powerful feelings.
— free-flowing in structure.
Hungarian Rhapsody No. 2 (Liszt)
Classical music genres
Symphony
— is a piece of music almost always written for an orchestra to play.
— The work is usually divided into 3 or 4 movements.
Symphony No 5 in C minor, Op 67 (Beethoven)
Classical music genres
Concerto
— is a piece of music made for a solo instrument and an orchestra.
VIOLIN Concerto in A minor, BWV 1041 (JOHANN SEBASTIAN BACH)
— The work usually has 3 movements: a fast one, a slow one and a fast to finish with.
Classical music genres
Opera
The Magic Flute – Queen of the Night aria (Mozart)
Classical music genres
Ballet
Swan Lake – Dance of the cygnets (Tchaikovsky)
Classical music genres
Soundtracks
recorded music accompanying and synchronized to the images of a motion picture, book, television program, or video game.
Thank you!